PTCA
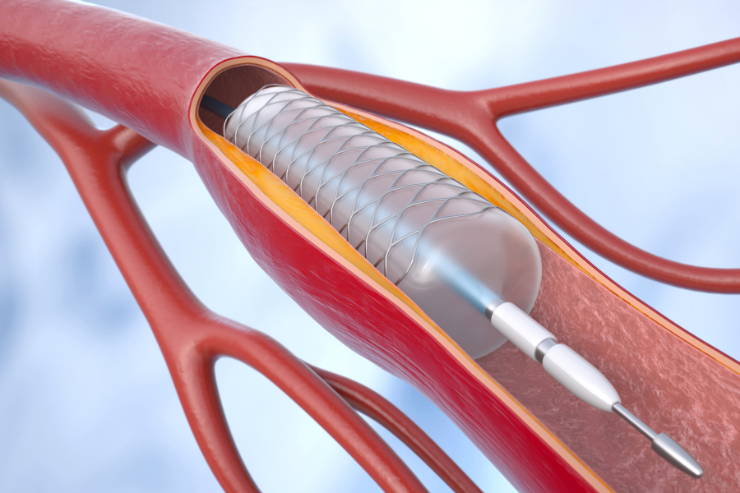
PTCA, or Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty, is a specialized procedure used to treat narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. It is designed to improve blood flow to the heart muscle, which can relieve symptoms of coronary artery disease, such as chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath, and reduce the risk of heart attacks.
How Does PTCA Work?
The PTCA procedure starts with the insertion of a catheter through a small incision, typically in the groin or wrist. The catheter is advanced to the coronary artery under X-ray guidance. A small balloon at the catheter’s tip is then inflated at the site of the blockage or narrowing. This balloon expands, compressing the plaque against the arterial walls and widening the artery to restore normal blood flow. Often, a stent—a small, mesh-like tube—is also placed to keep the artery open after the balloon is deflated and removed.
Types of PTCA
- Balloon Angioplasty: Utilizes a balloon to widen the narrowed artery.
- Stent Placement: Involves the placement of a stent to maintain arterial openness and prevent re-narrowing.
- Drug-Eluting Stent: A type of stent that releases medication to minimize the risk of re-blockage.
Benefits of PTCA
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure is less invasive compared to open-heart surgery, leading to quicker recovery times and shorter hospital stays.
- Effective Relief: PTCA can significantly alleviate symptoms of coronary artery disease, enhancing overall heart function.
- Improves Quality of Life: By restoring normal blood flow, PTCA helps patients return to their daily activities and reduces the risk of severe cardiac events.
Why Choose PTCA?
PTCA is a well-established treatment for coronary artery disease that offers significant benefits, including symptom relief, improved heart function, and a reduced risk of heart attacks. Its minimally invasive nature allows for faster recovery and a quicker return to daily activities, making it a preferred choice for many patients with coronary artery issues.
